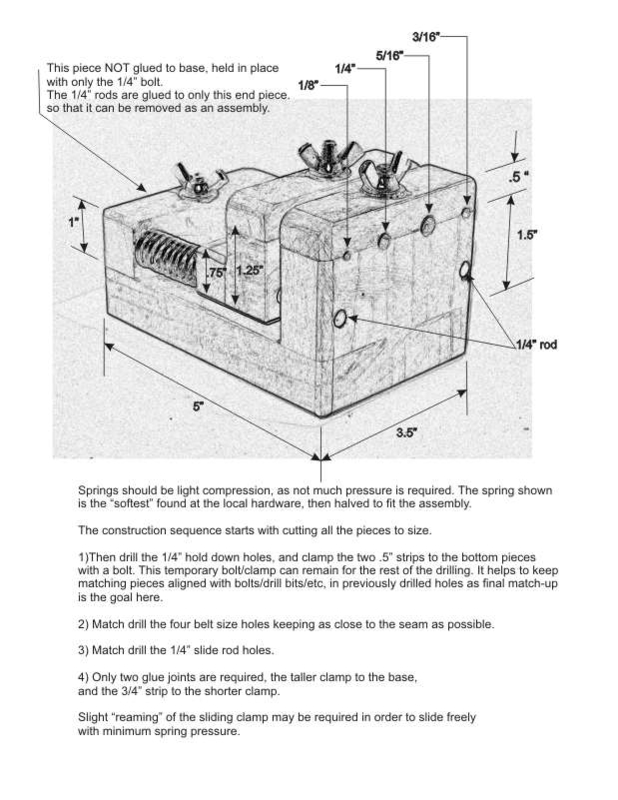
Rubber
Overview
Rubbers
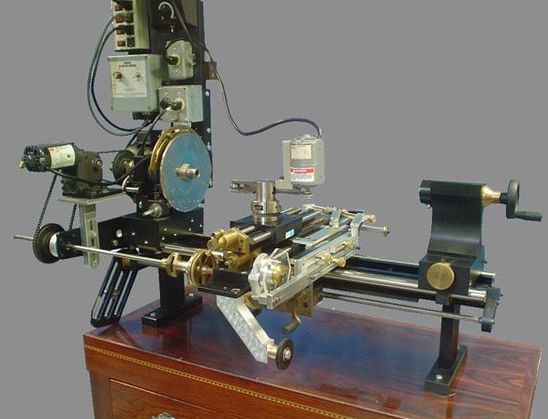
Image courtesy OrnamentalRoseEngine.com
Rubbers (sometimes called Touches) are so called as they rub against the rosettes. The terms are interchangeable, but Touch is preferred by some.
A rubber works fundamentally the same way a cam follower does on an engine, except in the opposite way.
- On an internal combustion engine, the cam follower moves based on the cam's shape.
- On a rose engine lathe, the the rubber is fixed, and the rosette moves the shaft to which it is attached, based on its own shape.
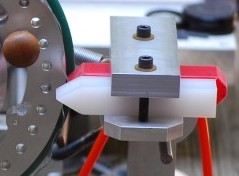
Two are shown in the picture to the right : the red and white pieces of plastic (only the red one is engaged with the rosette at this time).
Rubbers come in various forms or shapes, and each can produce a different result. Commonly used ones are :
- Pointed (with a small rounding on the end to minimize damage to the rosette),
- Bearing ended, where the bearing rides on the rosette, and
- T-shaped, where the wide T smoothes out the undulations of the rosette.
On a typical rose engine lathe, as the shaft rotates the object and the rosette, the rosette moves against the rubber, moving the shaft. The rubber stays fixed, making the whole headstock move according to the rosette's shape. As shown, this would cause a rocking motion.
I say "typical" as there are a class of rose engine lathes which have a fixed headstock, and the cutter moves according to the rosette. This is the Pudsey-Dawson approach, and the Paul Cler lathe is an example of this.
Recently, this approach is becoming more prevalent with the ready availability of linear bearings at a low cost. At the 2018 Ornamental Turners International Symposium, one demonstrator had a self-built rose engine lathe using this approach.
Examples of this device in use
This YouTube video shows rocking movement, along with differently shaped rubbers. I don't know the language used; but the video does show the movement well.
Usage Notes
Ray Simmons noted that a rubber with a large radius effectively works as an amplitude adjuster by smoothing out the ups and down of the lobes.
Norman Tweddle noted in his book, The Rose Engine Lathe, that the rubber should be opposite the cutter to ensure that the rubber stays engaged with the rosette.
More Information
Published Articles
- Of Rubbers and Rosettes, by David Lindow. Rose Engine News, Volume 3, No. 1 - Spring-Summer, 2012, pg, 10
- Patterns On Side Grain Produced From Sine Waves, by John Tarpley. Rose Engine News, Volume 4, No. 1 - Spring-Summer, 2013, pg, 20
- Rosettes, by (unknown). Part about rubbers starts on pg. 5. Rose Engine News, Volume 4, No. 2, Tool Bonus Issue, 2014, pg, 3.
Books
- The Rose Engine Lathe, by Norman Tweddle.
Web Sites

- The Santa Fe Symposium is an annual conference for jewelry makers, and often has topics around ornamental turning and especially guilloché. These include a bit of history and are great reads. One of note includes:
- The Parts and Processes of a Rose Engine in the Modern Shop by G. Phil Poirier, 2016. Pages 483-484 show a great overview of the effect on a rubber's radius vs. the shape of the rosette.
Presentations
- Eddie Bell gave a presentation, Variations on the Gorst Finial at the 2018 Ornamental Turners International Symposium. This is a nice presentation about the effect rubbers can have on the object shape.
- OTI member meeting, "A Rose of a Chat", 21 January 2025. Steve White gave a great presentation at the effect of different rubber shapes. The presentation is available at the [[https://www.ornamentalturners.org/content.aspx?page_id=0&club_id=911167 | OTI web page]. Steve particularly addressed using rollers in the working end of the rubber.
|
Disclaimer: eMail comments to me at OTBookOfKnowledge @ Gmail.com. The process of woodturning involves the use of tools, machinery and materials which could cause injury or be a health hazard unless proper precautions are taken, including the wearing of appropriate protective equipment. |